Diabetes Care: Mastering Medication Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Effective diabetes management is essential for preventing complications and maintaining a good quality of life. Medication therapy plays a crucial role in controlling blood sugar levels and managing diabetes.
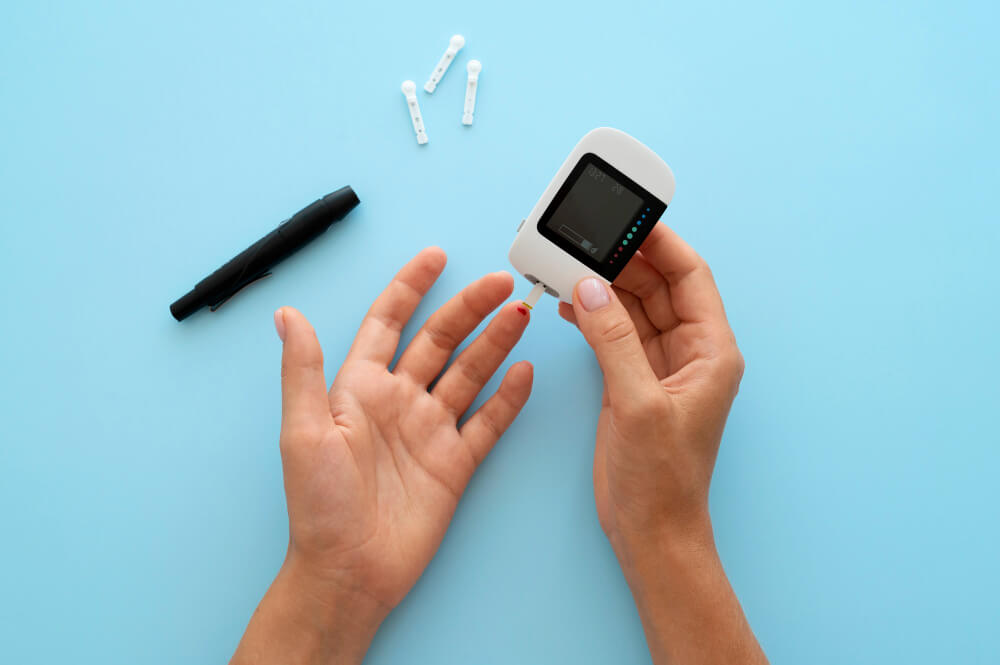

The Importance of Medication Management
Medication management is a cornerstone of diabetes care. By taking your medications as prescribed and following your doctor’s instructions, you can:
- Control Blood Sugar Levels Maintain your blood sugar within a target range to prevent complications.
- Reduce the Risk of Complications Lower your risk of developing diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease.
- Improve Quality of Life Effective blood sugar control can help you feel better and live a more active life.
Types of Diabetes Medications
There are several types of medications used to treat diabetes, each with its own unique mechanism of action. Common types of diabetes medications include:
Insulin A hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin injections are often necessary for people with type 1 diabetes and may also be required for people with type 2 diabetes.
Oral Medications There are several classes of oral medications used to treat type 2 diabetes, including:
- Biguanides
- Sulfonylureas
- Thiazolidinediones
- DPP-4 inhibitors
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- SGLT2 inhibitors
Developing a Medication Management Plan
Your doctor will work with you to develop a personalized medication management plan that is tailored to your specific needs. This plan will typically include:
- Medication Dosage Determining the appropriate dosage of your medications.
- Timing of Medication Scheduling your medications throughout the day to maintain consistent blood sugar control.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels to assess the effectiveness of your medications.
Adhering to Your Medication Regimen
Adhering to your medication regimen is essential for effective managing diabetes. This means taking your medications as prescribed, even if you feel well.
Tips for Adherence Here are some tips for adhering to your medication regimen:
- Set reminders to take your medications.
- Keep a medication log to track your doses.
- Talk to your doctor about any side effects you may experience.
Monitoring Your Blood Sugar
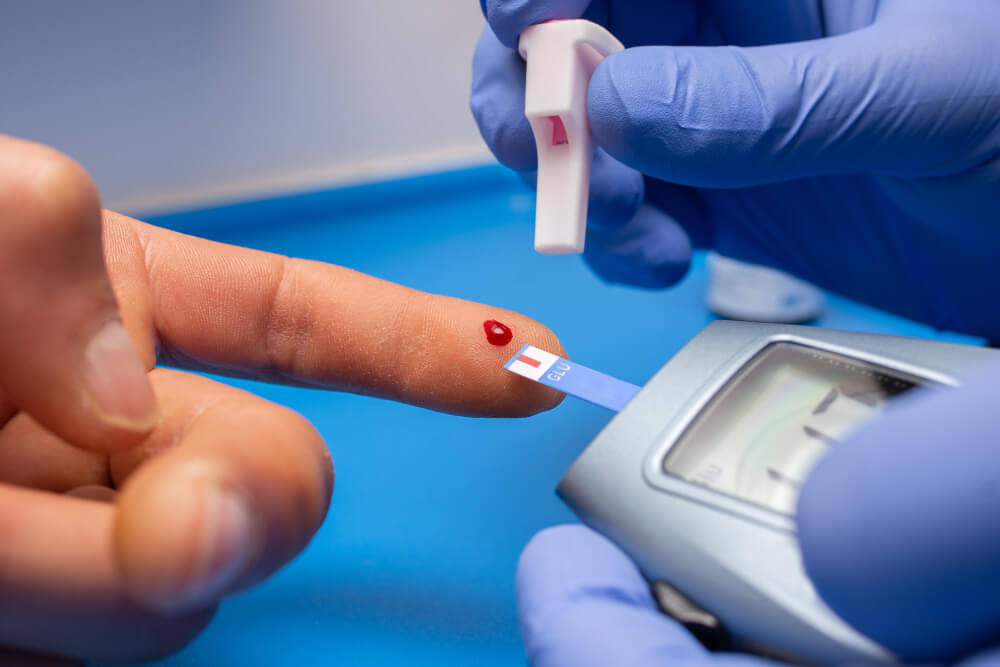
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is crucial for managing diabetes. This involves using a blood glucose meter to test your blood sugar at home.
- Blood Sugar Targets Your doctor will set target blood sugar levels for you to aim for.
- Adjusting Medications If your blood sugar levels are not within the target range, your doctor may need to adjust your medications.
- Recognizing Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia Learn the signs and symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and high blood sugar (hyperglycemia).
Lifestyle Factors and Diabetes Management
In addition to medication, lifestyle factors play a significant role in managing diabetes. These include:
- Healthy Diet Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Exercise Engaging in regular physical activity can help improve blood sugar control.
- Weight Management Maintaining a healthy weight can help improve blood sugar control and reduce the risk of diabetes complications.
- Stress Management Managing stress can help prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Complications of Poorly Managed Diabetes
If diabetes is not well-managed, it can lead to a variety of complications, including:
- Cardiovascular Disease Heart attack and stroke.
- Kidney Disease Damage to the kidneys.
- Nerve Damage Neuropathy, which can cause numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Eye Problems Retinopathy, which can lead to vision loss.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you have diabetes or are concerned about your risk of developing diabetes, it is important to see your doctor for regular check-ups. Your doctor can help you manage your condition and prevent complications.
Signs of Uncontrolled Diabetes Signs of uncontrolled diabetes may include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
Effective diabetes management requires a comprehensive approach that includes medication therapy, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. By working closely with your primary care physician, you can take control of your diabetes and improve your overall health and well-being.
Contact us for Tailored medication management plans for diabetes care (972) 633-8747 Or (972) 848-0873 Or visit us https://www.sccplano.com/locations/east-plano/
